Image by seagul from Pixabay
Graphene nanotechnology can be used as an incredibly intelligent and effective coolant across a range of industries. However, is it the most effective solution on the market? In this post, find out how it stacks up against the current market-leading solutions.
The Impossible Has Become Commonplace
Modern technology is making the seemingly impossible an everyday reality. For example, our smartphones now unlock with face recognition. Quite likely, you run your business from a tablet. What’s more, your headphones can sense when they’re on your head, thereby playing and pausing the music.
These small things may seem insignificant now because we use them every day. However, 20 years ago none of these things would have seemed plausible.
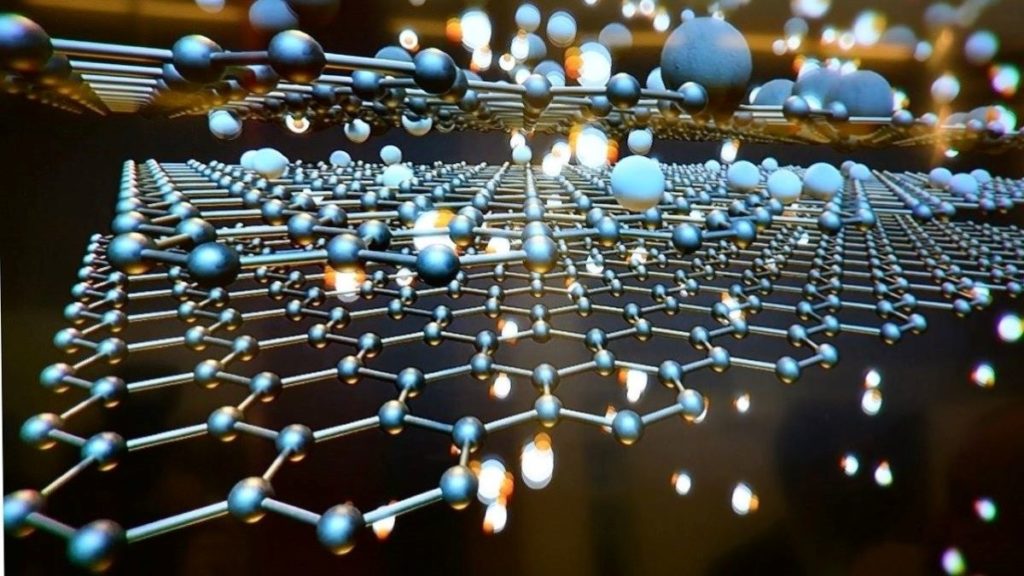
One of the most exciting of these recent technological advancements is the progression of graphene nanotechnology. Once simply one of the latest headlines in the field of scientific discovery, it is now transitioning into commercial use. In fact, several real-world applications have already been realized.
Today, graphene nanotechnology is an incredibly intelligent and effective coolant across a range of industries. However, is it the most effective solution on the market? Find out how it stacks up against the current market-leading solutions we discuss here.
RELATED ARTICLE: BUSINESS AND TECHNOLOGY IDEAS FOR CITIES OF THE FUTURE
What Is Graphene Nanofluid?
To begin with, graphene is a form of carbon. Its interlocking atoms create an incredibly thin yet durable material. First isolated at the University of Manchester in 2004, graphene is one of the most innovative and exciting discoveries of this century due to its potential applications.
For example, its multiple capabilities include heat conduction. Graphene is 10,000 times more effective at conducting heat than water. This opens the door to thousands of possibilities for large- and small-scale cooling.
Graphene nanofluids are a family of fluids that scientists have enhanced using nanotechnology. These enhancements allow various industries to use them in processes that require high-heat transfer.
For example, industries such as automotive, high-performance computing, and industrial systems have all put graphene nanofluids to use.
What Are the Advantages of Graphene Nanotechnology?
When compared to other cooling solutions, graphene nanotechnology is a highly advantageous feature to embed into your blueprints. This is because it is a more effective coolant in almost any design with high-heat areas.
Additionally, the patented technology by Flexegraph offers around 30-80% improved heat exchange in comparison with other market-leading technologies. This creates the environment for unrivaled performance when applied to high thermal loads.
In terms of the eco-friendly philosophies behind the application of graphene, Flexegraph’s solution manages to cover all the bases. In fact, it’s a non-toxic technology that can be utilized for sensitive applications. Moreover, graphene’s heat conduction properties lead to fewer restrictions due to the thermal limits in the automotive industry. This enhances performance in the most environmentally friendly way possible.
How Else Are Nanofluids Used?
While it is mostly the automotive and high-powered computing industries that use graphene nanofluids, there are far more ways in which nanofluids can be used. In fact, nanofluids have the potential to revolutionize standards across multiple industries in the future.
To this end, Flexegraph has designed a flexibly formulated solution that’s entirely scalable. Plus, it provides compatibility with existing additives and components. This makes the coolant incredibly versatile. It’s poised to become the “Intel Inside” of the liquid cooling market.
Better Heat Management Means Lower Costs
This more efficient solution can help reduce costs in both the production and maintenance of products that require extensive cooling. Better heat management equals a more efficient system, lower costs, and a smaller carbon footprint.